
The urgency of addressing climate change necessitates a global shift towards a decarbonized future. This article explores the path of decarbonization, outlining a comprehensive, integrated strategy to achieve net-zero emissions.
Impact of Global Warming
On January 12, 2024, the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), stated: “Not only was 2023 the warmest year in NOAA’s 174-year climate record — it was the warmest by far… We will continue to see records broken and extreme events grow until emissions go to zero”.
The impact of these records is very clear for everyone to see. There is much news about disasters related to global warming, including droughts, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events every day. Furthermore, these disasters are increasingly affecting not only global citizens, but also companies and public organizations, with extremely high economic and human costs.
The effect of these records is readily apparent to all. Every day, there is a lot of news coverage of natural calamities linked to global warming, such as droughts, increasing sea levels, and extreme weather. Moreover, these catastrophes have exceptionally significant financial and human costs. It impacts not only global residents but also businesses and governments.
The reason for the rising temperatures that everyone is aware of is attributed to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions related to human activities. Specifically, it is not just transportation relying on fossil fuels, heating residential areas, construction, and industry, but also agriculture releasing methane gas. These emissions are accumulating in the atmosphere faster than natural carbon sinks – such as oceans and forests – can absorb them. This is why integrated strategies are necessary to ‘decarbonize’ our economy. Recognizing the importance of decarbonization, we must address activities that will lead to a significant reduction in emissions and ultimately eliminate the warming GHGs.
Technology is rapidly advancing, and several key strategies are being implemented in an integrated manner that can help achieve the decarbonization process.

The Crucial Role of Decarbonization
CO2 emissions, or carbon dioxide emissions, refer to the release into the atmosphere by human activities such as building, transportation, manufacturing, and energy generation. This gas which comes from both residential and industrial activities, is a major contributor to global warming and climate change.
Besides, as the name suggests, decarbonization is the process of reducing or eliminating greenhouse gas emissions through the phase-out of fossil fuel use and the use of renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and geothermal heat. It is the main force behind the energy transition, which is essential to halting global warming.
The path of decarbonization consists of many strategies that can support achieving the goal of zero emissions, and then reducing the worst consequences of global warming and climate change.
The electrification of business and household activities is the first step and an additional step is investing in clean energy production. Although electrification is the ultimate purpose, using sustainable energy sources is still important to achieving it
Energizing the economy through increased coal or natural gas burning will not tackle the greenhouse gas issue; instead, it will simply transfer it from consumers to producers. Therefore, the electrification process must rely on renewable sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal.
Additionally, integrating digital technologies and Internet-of-Things (IoT) applications is crucial. These advancements will enhance energy efficiency, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions and enabling businesses, governments, and individuals to cut down on energy costs.
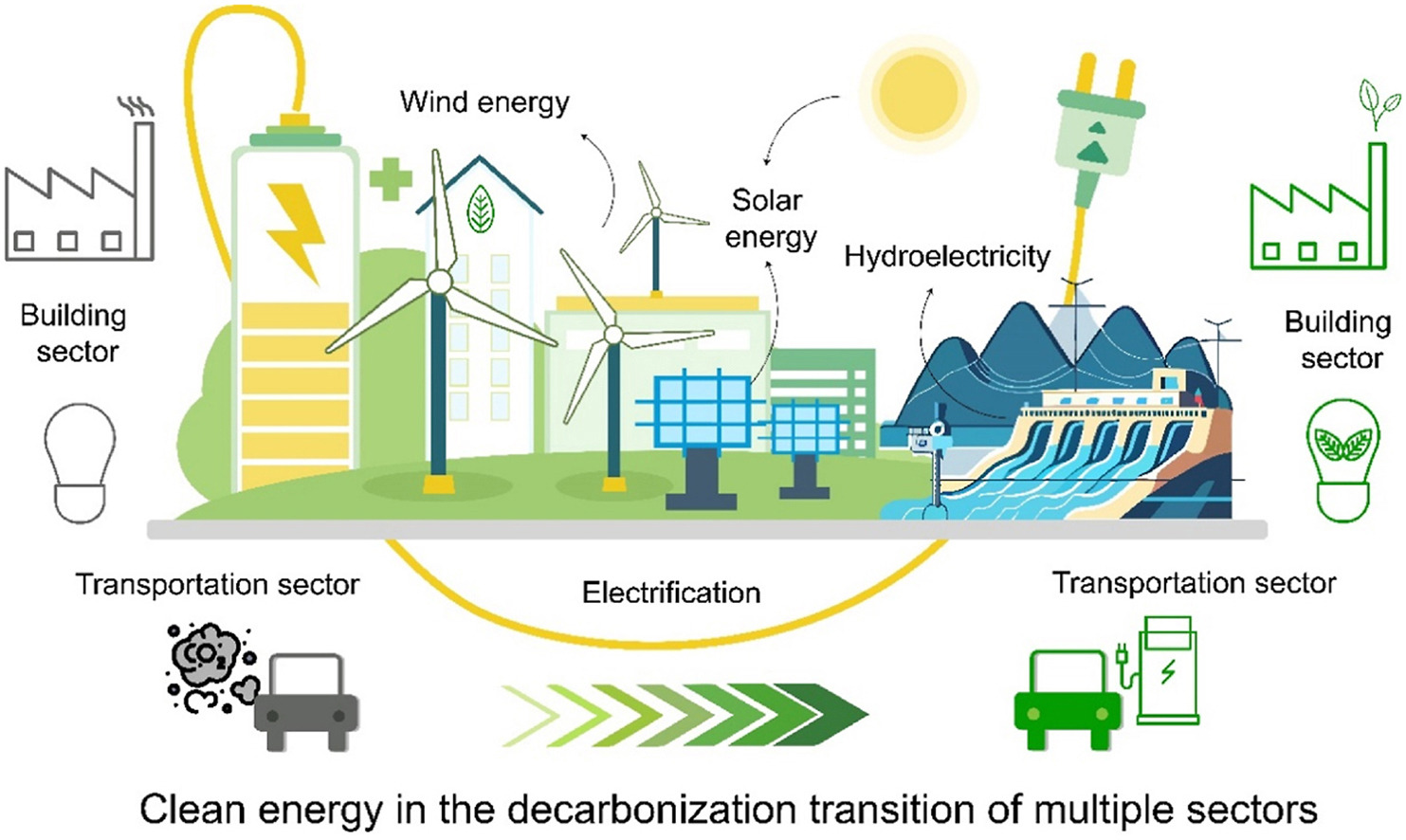
The Decarbonization and Energy Transition Process
Numerous factors need to align in order for humanity to solve climate change effectively and shift the trajectory of global warming. Of all these elements, two are especially significant: decarbonization and the energy transition. This transition involves transforming the global energy industry from reliance on fossil fuels such as oil, natural gas, and coal to renewable sources like solar, wind, geothermal, and clean hydrogen. Additionally, enhancing efficiency in energy generation, distribution, and usage plays a critical role in significantly cutting down on emissions that contribute to climate change.
According to The United Nations, the energy transition is a crucial step towards limiting the rise in global temperatures to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, in line with the Paris Agreement’s objectives.
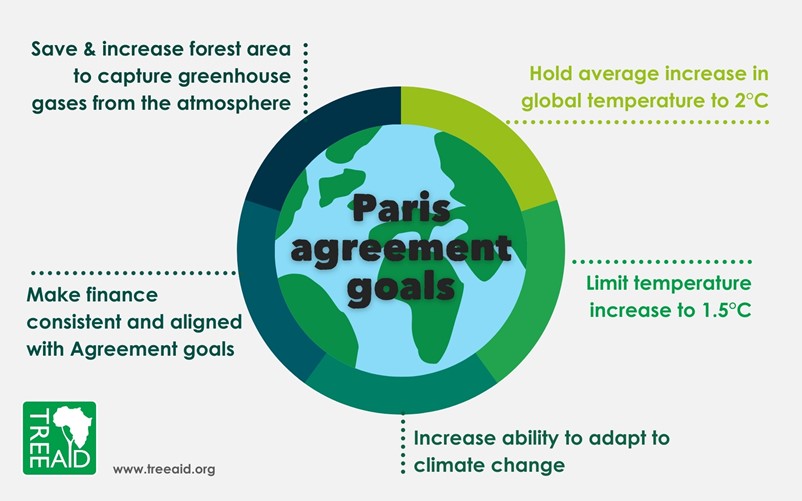
To achieve this, a substantial 45% reduction in global greenhouse gas emissions by 2030, reaching net zero emissions by 2050, is essential. Fulfilling these targets is deemed vital in tackling the adverse impacts of climate change.
Conclusion
Overall, the urgency to combat climate change and shift towards a decarbonized future is clear. The impact of global warming is undeniable, with records of extreme weather events and rising temperatures becoming more frequent and severe. The crucial role of decarbonization in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to renewable energy sources is paramount in addressing the challenges posed by climate change. The integration of sustainable practices is the key strategy in achieving zero emissions and mitigating the effects of global warming.
The transition to a decarbonized economy and energy system is essential to limit global temperature rise and combat the adverse impacts of climate change. Also, it emphasizes the need for concerted global efforts to reach net zero emissions by 2050.


